Chagas Disease
CHAGAS DISEASE
It is a parasite induced infection caused by bugs and spreading to humans.
Chagas disease is caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, which is transmitted to animals and people by insect vectors and is found only in the America, so therefore also called American trypanosomiasis.
It is usually seen in swamp areas and rural areas of Latin America.
It is estimated that as many as 8 million people in Mexico, Central America, and South America have Chagas disease, most of whom do not know they are infected. If untreated, infection is lifelong and can be life threatening.
Transmission:-
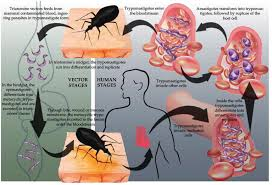
It is spread via bugs which pass on the vector in the healthy humans after biting them.
Parasite- Trypanosoma cruzi (found in feces)
Insect vector- Triatomine bugs also called kissing bugs
These blood-sucking bugs get infected with T. cruzi by biting an infected animal or person. Once infected, the bugs pass the parasites in their feces. The bugs are found in houses made from materials such as mud, adobe, straw, and palm thatch. During the day, the bugs hide in crevices in the walls and roofs. During the night, when the inhabitants are sleeping, the bugs emerge. they usually poop(defecate) on the sleeping individual and during sleep the person may scratch leading to its entry in blood, skin, eye, or mouth.
People also can become infected through
- Congenital transmission (from a pregnant woman to her baby);
- Blood transfusions;
- Organ transplantation;
- Consumption of uncooked food that is contaminated with feces (poop) from infected triatomine bugs; and
- Accidental laboratory exposure.
- Fever
- Malaise
- Loss of appetite
- Back pain
- Muscle aches
- Metallic taste
- Swelling of eyelid, near the wound
- Headache
- Rashes
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Peripheral Blood Smear examination
- Specific parasite antibody testing
- Benznidazole
- Nifurtimox






Comments
Post a Comment