Tuberculosis
TUBERCULOSIS INFECTION
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by bacteria named Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Primarily, it is known that it affects lungs, but the spread of infection can be dangerous and to the sites like liver, kidney and even to brain.
Spread of bacteria:-
It is an air-borne infection. When an infected person coughs or sneezes or speaks or even sings, the droplets released and hence inhaled by healthy individual can lead to the spread.
Misconceptions about its spread:-
TB is NOT spread by
- shaking someone’s hand
- sharing food or drink
- touching bed linens or toilet seats
- sharing toothbrushes
- kissing
Pulmonary TB
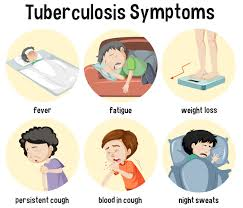
- a bad cough that lasts 3 weeks or longer
- pain in the chest
- coughing up blood or sputum (phlegm from deep inside the lungs)
Effect of TB on metabolism and growth:-
- weakness or fatigue
- weight loss
- no appetite
- chills
- fever
- sweating at night
Risk factors for TB:-
- HIV infection (the virus that causes AIDS)
- Substance abuse
- Silicosis
- Diabetes mellitus
- Severe kidney disease
- Low body weight
- Organ transplants
- Head and neck cancer
- Medical treatments such as corticosteroids or organ transplant
- Specialized treatment for rheumatoid arthritis or Crohn’s disease
There are vaccines available which is usually administered in childhood and infancy stage with the name of BCG.
Sometimes, vaccines are not enough to protect one immune system from it.
It is done in 2 ways i.e. either via skin or blood
TB Skin test/Mantoux Tuberculin test- In this, a fluid named tuberculin is injected in the lower part of the arm and results are awaited in 48-72 hours.
TB blood test:- It is also called interferon-gamma release assays.
Chest X-ray
Sputum culture
Treatment of TB Infection:-
This treatment usually takes 6 to 9 months as per the severity of symptoms and recovery.
DOT Therapy
This is a 4 drug regimen namely:
-Isoniazid(H)
-Rifampicin(R)
-Pyrazinamide(Z)
-Ethambutol(E)
5th drug was added by WHO in case of bacterial infection which was
-Streptomycin(S)
There are certain topics which is still unknown to common people which are:-
Drug resistant TB:- It is seen when the bacteria becomes resistant to treatment and situations involving this are:-
- People do not complete a full course of TB treatment
- Health care providers prescribe the wrong treatment (the wrong dose or length of time)
- Drugs for proper treatment are not available
- Drugs are of poor quality
In this people do not feel sick
Not contagious
No treatment required
Tests may become positive









Comments
Post a Comment